Most AE Techron linear amplifiers can be customized via DIP switches
A DIP switch, which stands for dual in-line package, is a manual electric switch that is designed to be used on a printed circuit board along with other electronic components. It is commonly used to customize the behavior of an electronic device for specific situations.
AE Techron’s linear amplifiers, 7224, 7234, 7548, 7794, 7796, and 7796HC, all share the same DIP switch configurations. This flexible design allows your clients to choose from a range of field-configurable options, including:
- Operate as a stand-alone amplifier or as part of a multiple-amplifier system.
- Select DC-coupled or AC-coupled operation.
- Select Controlled-Current or Controlled-Voltage modes of operation.
- Enable a 50-kHz low-pass filter.
- Change the maximum amplifier gain from 20:1 to 6:1.
- Operate with variable gain control or at a fixed gain setting (20 or 6).
- Electronic gain matching in parallel multi-amplifier configurations.
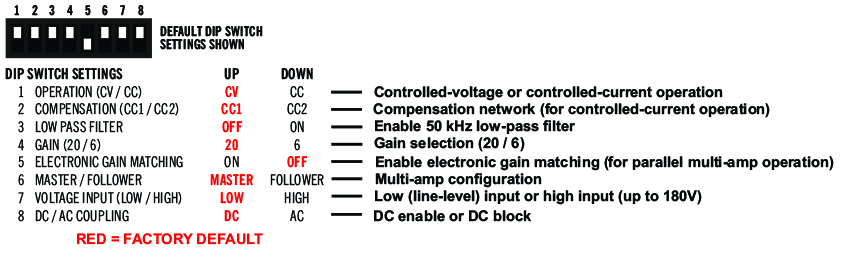
DIP Switch Configurations
In this Feature Focus we will highlight the eight DIP switch configurations available on our linear amplifiers. For more detailed information, you can access the unit operator’s manual which is available as a PDF on the individual product pages.
SW#1: Operation (CV/CC)
The default Up position is Controlled-Voltage mode, and the amplifier’s output voltage will be controlled by its input voltage signal. In the Down position, the amplifier will operate in Controlled-Current mode, with the output current being controlled by the input voltage signal.
SW#2: Compensation (CC1/CC2)
When the Compensation switch in the default Up position, the factory-installed RC network (CC1) is enabled. This network consists of a 68.1 kΩ resistor in series with a 47 nF capacitor. Placing the DIP switch in the Down position selects the CC2 network, which is unpopulated, but can be populated with a custom compensation network to fit your client’s requirements.
SW#3: Low-Pass Filter
The Low Pass Filter function inserts a 50 kHz (3-dB down) low-pass filter at the amplifier input to ensure that signals above 50 kHz are not amplified. The Low-Pass Filter DIP switch in the Up position (default) disables the low-pass filter. To enable the low-pass filter, place the DIP switch in the Down position.
SW#4: Gain (20/6)
When the Gain DIP switch is in the Up position (default), the amplifier’s maximum gain will be 20:1. Placing the DIP switch in the Down position will change the amplifier’s maximum gain to 6:1.
SW#5: Electronic Gain Matching
The Electronic Gain Matching function minimizes circulating currents when multiple amplifiers are used in a parallel configuration. When this switch is in the Down position (default), Electronic Gain Matching is disabled. When the DIP switch is in the Up position, the function is enabled.
When enabled, the Electronic Gain Matching function progressively increases impedance from the voltage gain as current increases, up to a maximum 0.10-ohm increase. This allows the amplifiers to operate in parallel without the use of separate ballast resistors in multi-amp applications up to 20 kHz.
SW#6: Master/Follower
When the Master/Follower DIP switch is in the Up position (default), the amplifier will function as a stand-alone amplifier or as a Master amplifier in a multi-amp system. When this switch is in the Down position, the amplifier will function as a Follower amplifier in a multi-amp system.
SW#7: Voltage Input (Low/High)
When the Voltage Input DIP switch is in the Up position (default), the voltage input is set to line level and the amplifier can be configured for use in a Parallel or Push/Pull multi-amp system, or as a Master amplifier in a Series multi-amp system. When this switch is in the Down position, voltage input is set to high, and the amplifier can be configured for use as a Follower amplifier in a Series multi-amp system.
SW#8: DC/AC Coupling
When the DC/AC Coupling DIP switch is in the Up position (default), the amplifier can receive and amplify both DC and AC signal. When this switch is in the Down position, a 2-Hz high-pass filter on the inputs prevents the transmission of DC signal.