Noise Floor, Load Type, Impedance, Bandwidth, Slew Rate
LINEAR VS SWITCH-MODE
With the introduction of AE Techron’s wide bandwidth (DC to 250kHz capable) switch-mode amplifiers, the question of which technology (linear or switch-mode) is better, is not as simple as it used to be.
Today, how do they compare?
NOISE FLOOR
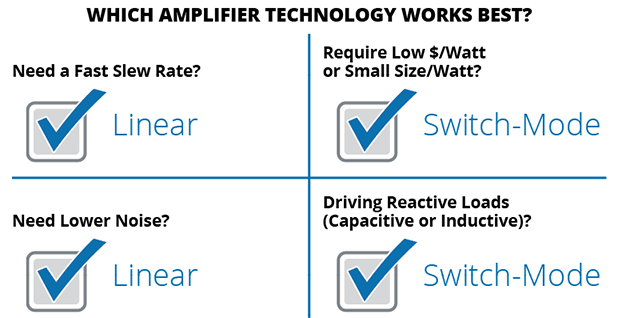
If noise floor is a critical requirement, a linear amplifier remains the clear choice. Lacking switching noises, noise floors in our linear amplifiers are measured in μV (7224 can be as low as 300 μV). This compares to switching noises that can exceed a mV in AE Techron switch-mode amplifiers, or multiple volts in our competitors’ low frequency, low bandwidth switch-mode amplifiers.
SLEW RATE
Linear amplifiers have a clear edge here as well. Switch-mode amplifiers need low pass filters to reduce switching noises, slew rates will be limited by these filters. In contrast, linear amplifiers have no high order output filters. Linear amplifier slew rates, especially when attempting short transitions like DC dropout or surges, can be as fast as 1.2 μS while even our fastest wide bandwidth switch-mode amplifiers are unable to produce signals with rise or fall times faster than 7 μS.
BANDWIDTH
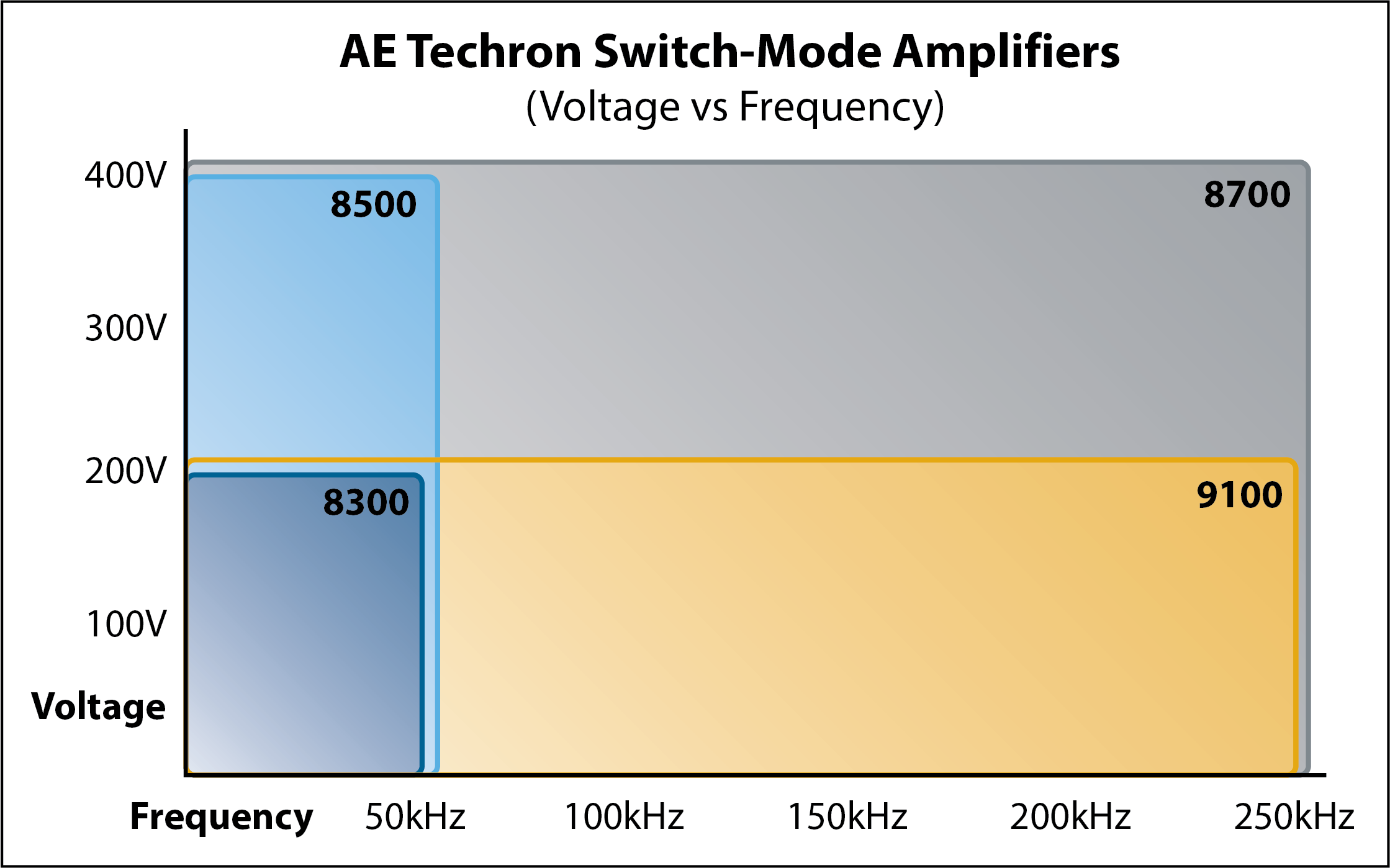
Linear amplifiers tend to have reduced power output as frequency increases, but the power decrease is gradual allowing them to produce small signal voltages to very high frequencies. Linear amplifiers are a great choice for applications where a small ripple voltage is needed at a very high frequency (EMC testing). In contrast switch-mode amplifiers will have full power to much higher frequencies. This gives our switch-mode amplifiers a big advantage for situations needing long term, high power above 50kHz and below 250kHz.
LOAD TYPE
Loads can be electrically described using two categories:
- Resistive
- Reactive (inductive or capacitive)
Linear and Switch-mode amplifiers react to these loads differently. Linear amplifiers are most efficient driving purely resistive loads, but their power outputs are reduced when driving reactive loads. Switch-mode amplifiers can produce greater effective power (kVA) for loads that are more reactive (inductive or capacitive).
IMPEDANCE
Linear amplifiers are very load impedance dependent. If a Linear amplifier is not well matched to the load, amplifier heat goes up and the maximum long-term output power is reduced. In contrast, switch-mode amplifiers maintain full power over a wide range of load impedances, with power output being limited by maximum amplifier voltage or current.
BENEFITS OF AE TECHRON SWITCH-MODE AMPLIFIERS
Our switch-mode amplifiers are the widest bandwidth switch-mode amplifiers in the world. They are able to produce more power, to higher frequencies, with faster slew rates, and lower ripple noises, than any other switch-mode amplifier.
For example, our new 9000 series can sustain 5000 watts at frequencies up to 250 kHz, effortlessly managing any load type, and any impedance. Think of applications like magnetic field coils, Helmholtz coils, and capacitor testing.
Linear and Switch-Mode amplifiers have different strengths, which tool is better depends on the characteristics of the problem being solved.
Product Links: