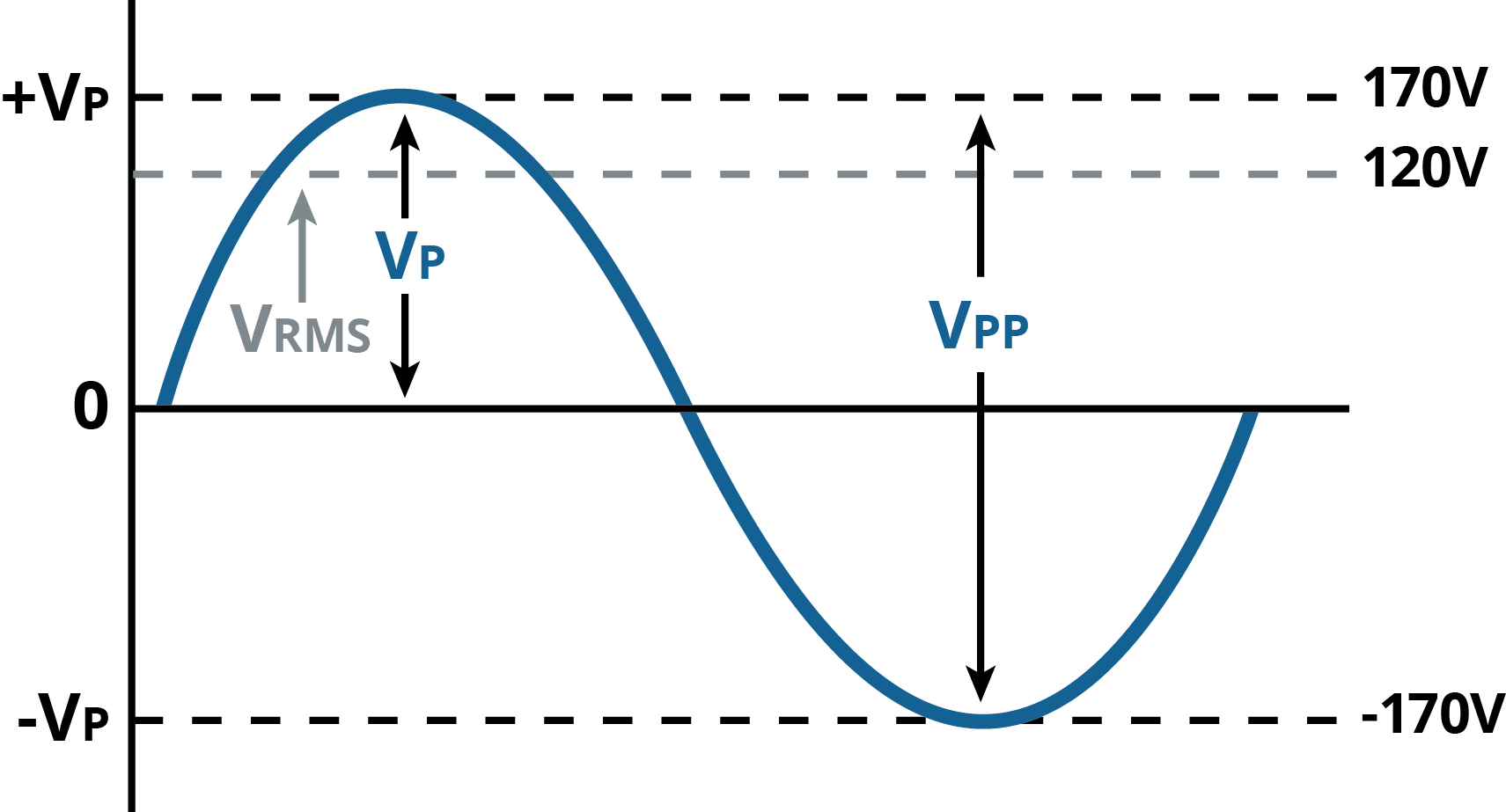
In the analysis of alternating current (AC) circuits, describing the voltage requires more than just a single value because the voltage is constantly changing over time. Three commonly used terms to characterize these time-varying voltages are Peak Voltage (VP), Peak-to-Peak Voltage (VPP), and RMS voltage (VRMS).
Peak Voltage refers to the maximum instantaneous voltage reached by the AC waveform, measured from the zero-volt reference level to the highest point. Think of it as the highest potential the voltage reaches during each cycle.
Peak-to-Peak Voltage, on the other hand, represents the total voltage variation between the positive and negative peaks of the waveform. For a sinusoidal waveform, VPP is simply twice the peak voltage.
RMS Voltage, or root-mean-square voltage, is the effective value of the AC waveform. It represents the DC voltage that would dissipate the same amount of power in a resistive load as the AC voltage.
Why are these different measurements important?
These different voltage measurements are crucial for various reasons in electronics, power systems, and power amplifiers. The understanding of an electrical source’s maximum, average, and minimum potential greatly enhances our design accuracy, functionality, and device performance
Peak Voltage is essential for determining the maximum voltage stress on components, which is critical for selecting appropriate insulation and voltage ratings. Exceeding a component’s peak voltage rating can lead to failure or damage.
Peak-to-Peak Voltage is useful in waveform analysis and amplifier design to understand the full range of the signal.
RMS Voltage is most widely used in power calculations and general AC electrical work because it represents the effective power delivery of the AC signal. It is the value typically provided for standard AC voltages like those in residential power outlets.
In simpler terms:
Imagine an AC voltage fluctuating between positive and negative values.
- The Peak Voltage is the highest point it reaches in either direction.
- The Peak-to-Peak Voltage is the total distance between the highest and lowest points.
- The RMS Voltage is a kind of average value that tells you how much “power” the AC voltage has in terms of its heating effect.
Example:
If you have a 120V RMS AC power supply, the peak voltage would be 120 * √2 ≈ 170V, and the peak-to-peak voltage would be 2 * 170V = 340V.
Key takeaways:
RMS voltage is used for power calculations and is often the value specified for AC power supplies. Peak and peak-to-peak voltages are important for understanding the voltage swing and ensuring components can handle the voltage levels.